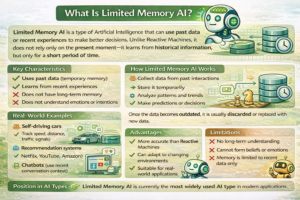
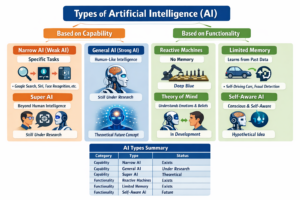
The evolution of self-aware AI starts with a simple but powerful idea: can a machine understand itself? For decades, computers only followed instructions. They calculated fast, sure, but they didn’t know they were doing it. Today, that line is starting to blur.
Self-aware Artificial Intelligence doesn’t mean robots with feelings like humans. Instead, it refers to systems that can model their own internal states, recognize limitations, and adapt behavior based on self-monitoring. In other words, the system has a form of digital self-reflection.
Defining Self-Awareness in Machines

In humans, self-awareness involves recognizing oneself as separate from the environment. For AI, it’s more technical. A self-aware system can:
- Monitor its performance
- Detect errors or uncertainty
- Adjust strategies without human input
This ability marks a major milestone in the evolution of self-aware AI, because it moves machines from reactive tools to adaptive partners.
Difference Between Intelligent and Self-Aware AI
Not all intelligent AI is self-aware. A chess engine can beat grandmasters, but it doesn’t know why it wins. Self-aware AI, however, can evaluate its own decision-making process. That distinction is crucial and often misunderstood.
Historical Evolution of Self-Aware AI
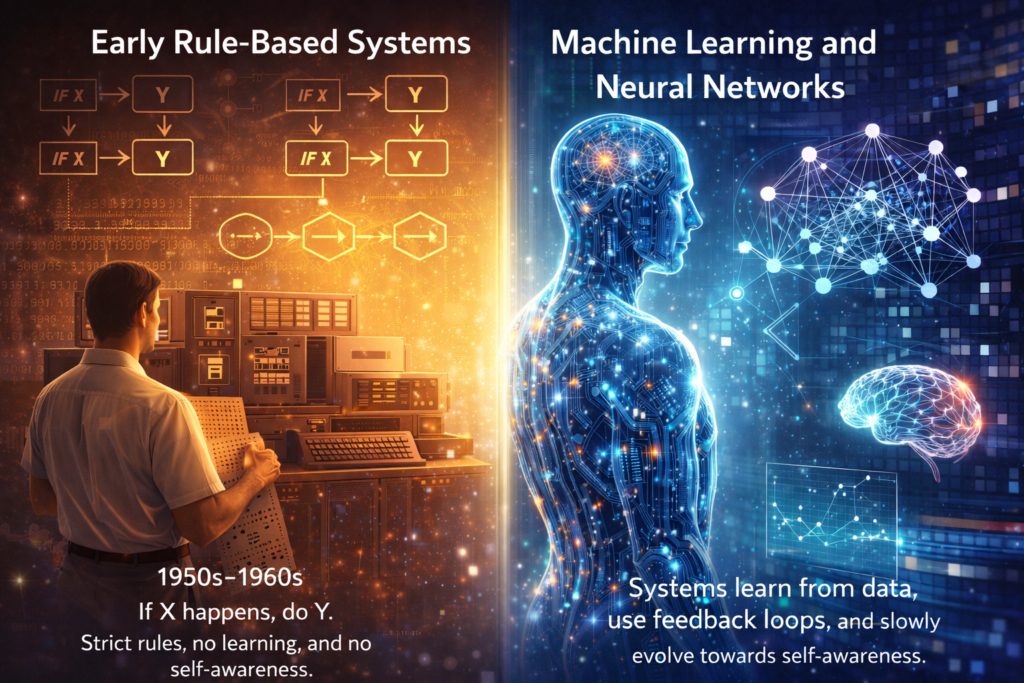
To appreciate the evolution of self-aware AI, we need to look back. Progress didn’t happen overnight. It came in waves, each building on the last.
Early Rule-Based Systems
In the 1950s and 1960s, AI systems followed strict rules. If X happens, do Y. These systems were predictable and brittle. They had no learning ability and zero awareness of their own actions.
Still, they laid the groundwork. Researchers began asking bigger questions, like whether machines could ever reason about themselves.
Machine Learning and Neural Networks
The real shift came with machine learning. Instead of hard-coded rules, systems learned from data. Neural networks, inspired by the human brain, allowed AI to recognize patterns and improve over time.
This phase accelerated the evolution of self-aware AI by introducing feedback loops. Systems could now evaluate outcomes and refine behavior, a small but vital step toward self-modeling.
Technological Foundations Enabling Self-Aware AI
Modern self-aware AI systems rely on several advanced technologies working together. These foundations make self-reflection possible.
Cognitive Computing
Cognitive computing aims to mimic human thought processes. It combines natural language processing, reasoning, and learning. Through this approach, AI systems can explain decisions and assess confidence levels.
IBM’s cognitive research is a good example of this direction (IBM AI Research).
Neuroscience-Inspired Models
Researchers also borrow ideas from neuroscience. Concepts like attention, memory, and metacognition are modeled in software. These models help AI systems “think about thinking,” which is central to the evolution of self-aware AI.
Ethical, Social, and Economic Impacts
As the evolution of self-aware AI continues, its impact reaches far beyond technology. It affects how we live, work, and trust machines.
Trust, Bias, and Transparency
Self-aware AI can flag its own uncertainty. That’s good news for safety and ethics. For instance, a medical AI that knows when it might be wrong can ask for human help.
However, concerns remain. Who controls these systems? How transparent are their self-assessments? These questions matter, and they’re being debated worldwide.
Workforce and Society
Automation already reshaped jobs. Self-aware AI could go further by managing tasks autonomously. While this raises fears, it also creates opportunities for new roles focused on oversight, creativity, and ethics.
Current Applications and Case Studies
The evolution of self-aware AI isn’t just theory. It’s already showing up in real-world systems.
Healthcare and Robotics
In healthcare, AI systems monitor their diagnostic accuracy. If confidence drops, they alert doctors. In robotics, machines assess their physical condition and adjust movements to avoid damage.
Virtual Assistants and Research Systems
Advanced virtual assistants can now evaluate whether they understood a request correctly. Research AI systems monitor experiment outcomes and refine hypotheses. These examples show practical, responsible self-awareness.
Future Outlook of Self-Aware AI
Looking ahead, the evolution of self-aware AI appears both promising and challenging.
Opportunities Ahead
Future systems may:
- Collaborate seamlessly with humans
- Improve safety in critical environments
- Accelerate scientific discovery
With proper design, self-aware AI could become one of humanity’s most helpful tools.
Risks and Safeguards
Still, safeguards are essential. Developers must set clear boundaries, ensure transparency, and keep humans in the loop. Optimism works best when paired with responsibility.