Artificial Intelligence is evolving fast, and honestly, it’s kind of mind-blowing. We’ve moved from simple rule-based systems to machines that can learn, adapt, and even surprise us. But now, a new and exciting concept is taking center stage: Theory of Mind AI. This form of AI isn’t just about crunching numbers or recognizing patterns. Instead, it’s about understanding people—their emotions, beliefs, intentions, and thoughts.
In the first phase of AI development, machines focused on tasks. They didn’t care why humans acted a certain way; they only cared what to do. However, as AI systems become more integrated into daily life, this limitation becomes obvious. Humans don’t operate purely on logic. We’re emotional, contextual, and sometimes unpredictable. That’s exactly where Theory of Mind AI comes into play.
Theory of Mind AI aims to bridge this gap by enabling machines to infer and respond to human mental states. As a result, AI becomes more relatable, trustworthy, and effective. From healthcare to education, and from robotics to customer service, the potential is massive. And yes, we’re only scratching the surface.
Understanding the Concept of Theory of Mind
Origins in Psychology and Cognitive Science
The term “Theory of Mind” didn’t originate in computer science. In fact, it comes straight from psychology. Researchers used it to describe the human ability to understand that other people have thoughts, beliefs, desires, and perspectives different from their own.
Children typically develop Theory of Mind around the age of four or five. Before that, they assume everyone thinks the same way they do. Once this ability develops, social interaction becomes far more nuanced. We start predicting behavior, empathizing, and communicating more effectively.
AI researchers borrowed this idea because, well, it works. If humans rely on Theory of Mind for smooth social interaction, then intelligent machines interacting with humans should probably do the same. Therefore, Theory of Mind AI is deeply rooted in cognitive science, neuroscience, and behavioral psychology.
What Is Theory of Mind AI?
Core Definition and Key Characteristics
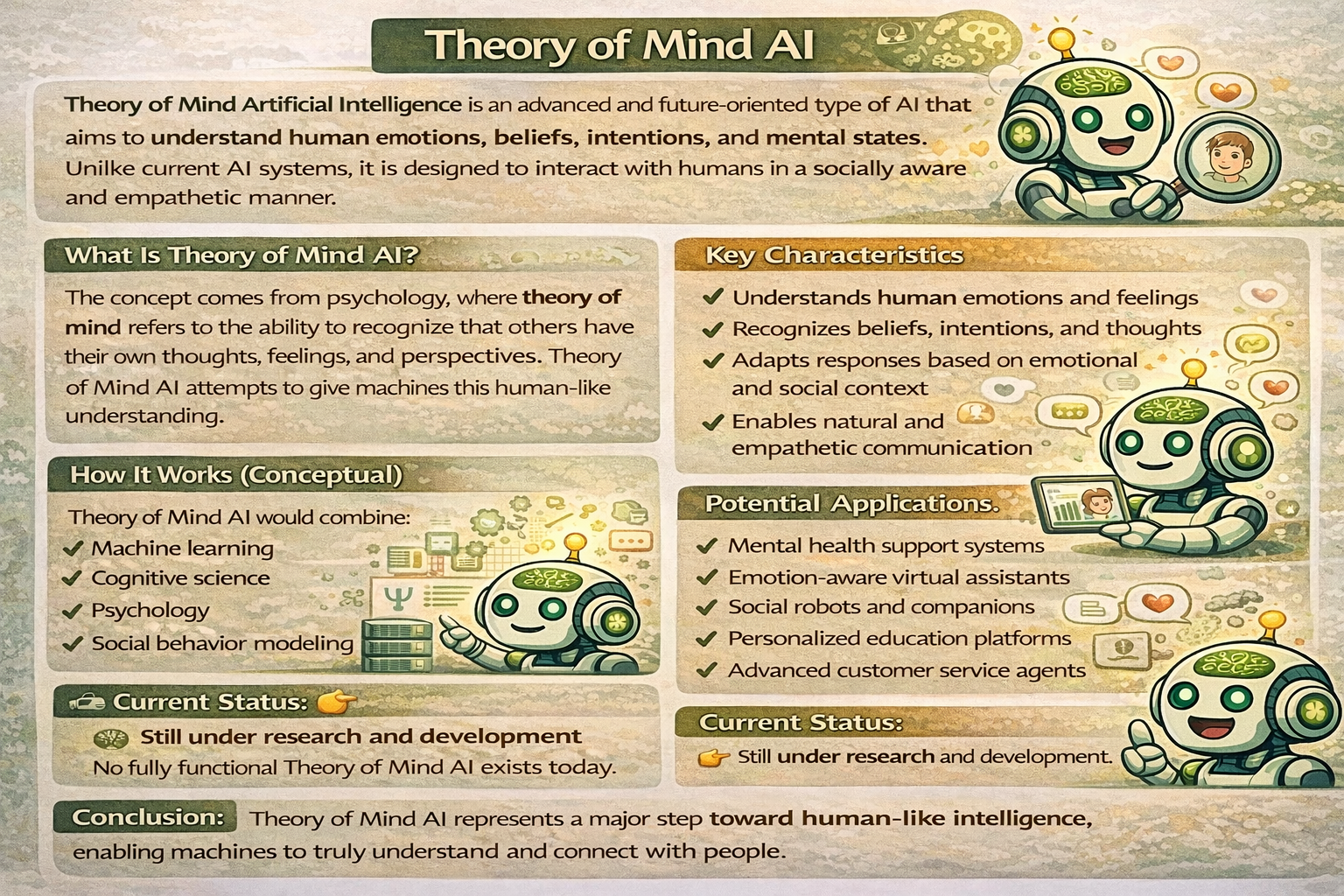
Theory of Mind AI refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to understand, model, and predict human mental states such as beliefs, intentions, emotions, and desires. Unlike traditional AI, these systems don’t just respond to commands. Instead, they interpret context and adapt accordingly.
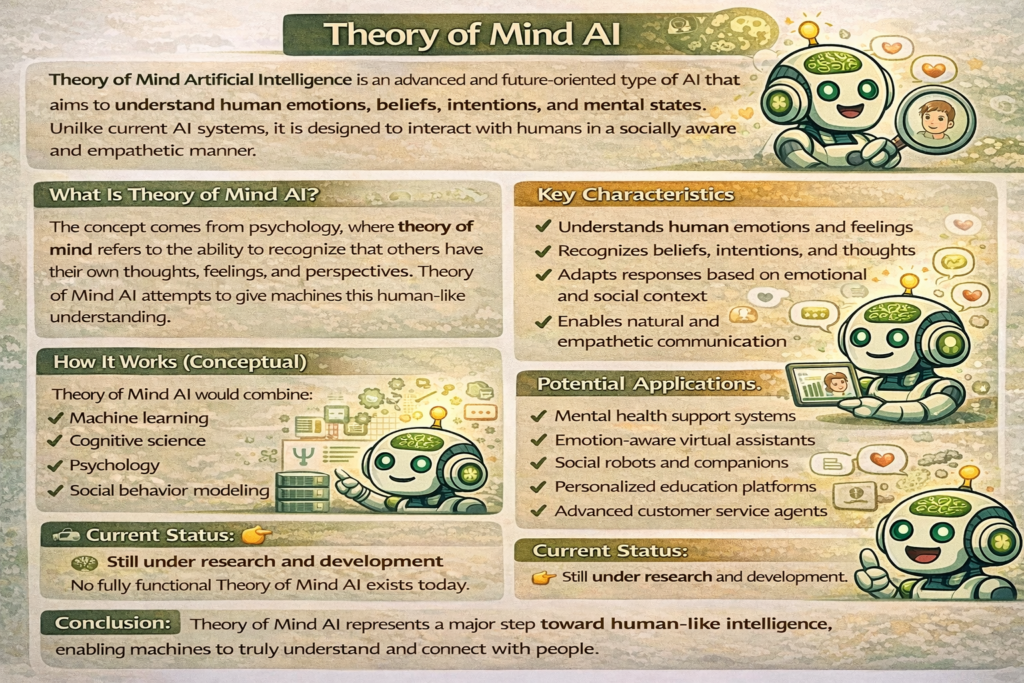
Some defining characteristics include:
- Ability to infer emotions from behavior and language
- Understanding that different users have different perspectives
- Predicting future actions based on mental states
- Adapting responses in socially appropriate ways
Difference Between Narrow AI and ToM AI
Most AI systems today fall under Narrow AI. They’re excellent at specific tasks like image recognition or language translation. However, they lack contextual understanding. Theory of Mind AI goes a step further.
| Feature | Narrow AI | Theory of Mind AI |
|---|---|---|
| Task Scope | Limited | Broad and contextual |
| Emotional Understanding | None | Emerging |
| Human Interaction | Functional | Socially aware |
| Adaptability | Rule-based | Context-driven |
In short, Narrow AI follows instructions. Theory of Mind AI understands intentions.
Why Theory of Mind AI Matters Today
Human–AI Interaction and Trust
As AI becomes more present in our lives, trust becomes a big deal. People are more likely to engage with systems that “get” them. If an AI assistant can sense frustration and adjust its tone, users feel heard. That’s not just nice—it’s essential.
Theory of Mind AI enhances communication by making interactions feel natural. It reduces misunderstandings and improves collaboration. In customer service, for example, AI that recognizes emotional cues can de-escalate tense situations more effectively.
Moreover, trust isn’t built overnight. It grows through consistent, empathetic interactions. Theory of Mind AI plays a critical role in making that possible.
How Theory of Mind AI Works
Cognitive Modeling and Mental State Attribution
At the heart of Theory of Mind AI lies cognitive modeling. This involves creating computational models that simulate how humans think and feel. These models analyze language, facial expressions, tone of voice, and behavior patterns to infer mental states.
For instance, if a user types quickly with negative language, the system might infer stress or frustration. Based on this, it can modify its response—perhaps by being more supportive or concise.
Role of Machine Learning and Neural Networks
Machine learning powers much of this process. Neural networks are trained on massive datasets containing examples of human interaction. Over time, the system learns associations between behavior and mental states.
Techniques commonly used include:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Sentiment Analysis
- Reinforcement Learning
- Multimodal Learning (text, audio, visual cues)
For deeper technical insights, you can explore research resources from organizations like MIT CSAIL (https://www.csail.mit.edu).
Applications of Theory of Mind AI
Healthcare and Mental Health
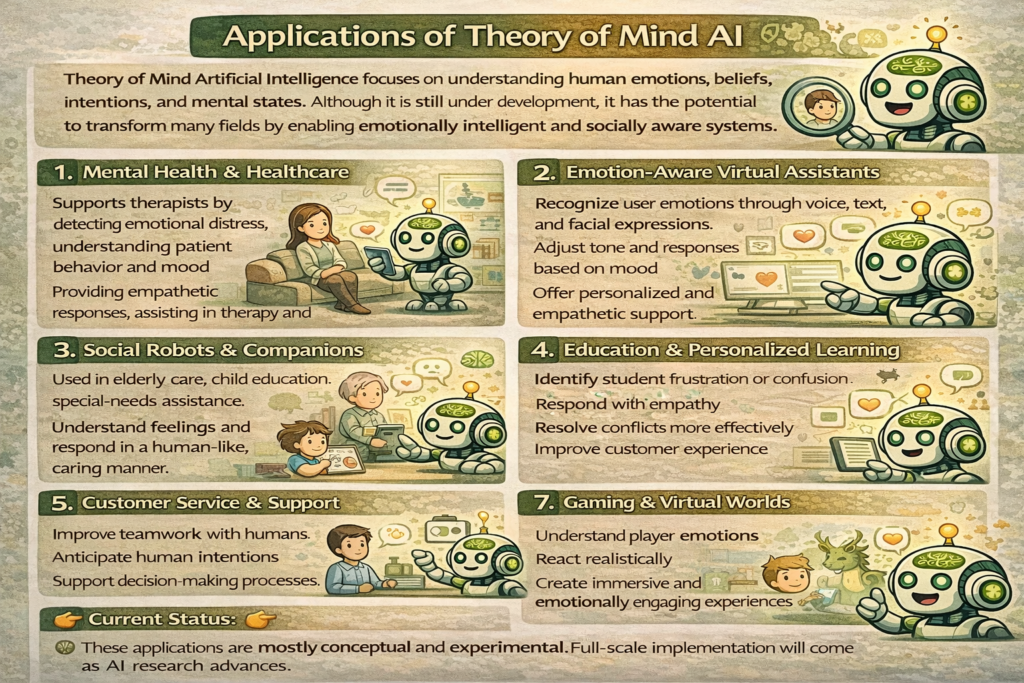
In healthcare, Theory of Mind AI can be a game changer. Virtual health assistants equipped with emotional intelligence can monitor patient mood, detect early signs of depression, and provide timely support.
Therapy chatbots, for example, can adjust their responses based on emotional cues. While they don’t replace human therapists, they offer accessible, immediate help.
Education and Personalized Learning
Education isn’t one-size-fits-all. Students learn at different speeds and in different ways. Theory of Mind AI can detect confusion, boredom, or enthusiasm, and adjust teaching methods accordingly.
This leads to personalized learning experiences that keep students engaged and motivated.
Robotics and Social Machines
Social robots benefit immensely from Theory of Mind AI. Whether it’s a companion robot for the elderly or a collaborative robot in the workplace, understanding human intentions improves safety and cooperation.
Benefits and Advantages of Theory of Mind AI
Theory of Mind AI offers several key advantages:
- Improved human–AI communication
- Higher user satisfaction and trust
- Better decision-making in social contexts
- Enhanced adaptability across domains
By understanding why people act the way they do, AI systems become more effective partners rather than mere tools.
Challenges and Limitations
Ethical, Technical, and Data Challenges
Despite its promise, Theory of Mind AI faces serious challenges. Modeling human emotions accurately is tough. Humans themselves don’t always understand their own feelings, so expecting machines to do so perfectly is unrealistic.
Ethical concerns also arise. If AI can infer mental states, privacy becomes a concern. Clear guidelines and transparency are essential.
Technical limitations include:
- Lack of high-quality labeled data
- Cultural differences in emotional expression
- Bias in training datasets
Addressing these issues is critical for responsible development.
Theory of Mind AI vs Other AI Types
Reactive Machines, Limited Memory, and Self-Aware AI
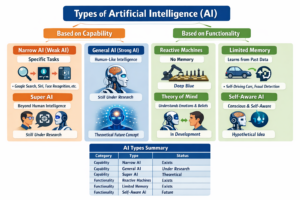
AI systems can be broadly classified into types:
- Reactive Machines – No memory, no understanding
- Limited Memory AI – Learns from past data
- Theory of Mind AI – Understands emotions and intentions
- Self-Aware AI – Hypothetical future stage
Theory of Mind AI sits at a crucial transitional stage. It brings us closer to truly intelligent systems without crossing into science fiction territory.
Current Research and Real-World Progress
Research in Theory of Mind AI is accelerating. Universities, research labs, and tech companies are investing heavily. While fully developed ToM AI isn’t mainstream yet, early implementations already show promise.
Progress is steady, and optimism is warranted.