Artificial Intelligence, often shortened to AI, is no longer a far-off idea from science fiction. It’s already part of our everyday lives. From voice assistants and recommendation systems to medical diagnostics and self-driving cars, AI is quietly shaping the modern world. When people talk about the types of artificial intelligence, they’re usually trying to understand how smart machines really are and what they can actually do.
At its core, artificial intelligence refers to machines that can mimic human thinking, learning, and problem-solving. However, not all AI systems are built the same. Some are extremely basic, while others aim to reach human-level intelligence in the future. That’s why understanding the different types of artificial intelligence is so important.
In this article, we’ll explore the major categories of AI in a structured, easy-to-read way. We’ll break down technical ideas into plain language, keep the reading level simple, and use real-world examples whenever possible. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of how AI is classified, why it matters, and where it’s all heading.
Understanding the Types of Artificial Intelligence
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence is the ability of a computer system to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence. These tasks include learning from data, recognizing patterns, making decisions, and understanding language. Instead of following only fixed rules, AI systems improve over time through experience.
According to widely accepted definitions, AI combines computer science, data, and algorithms to simulate human reasoning. A helpful reference on this topic can be found on Wikipedia’s Artificial Intelligence page:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence
Why Classifying AI Matters
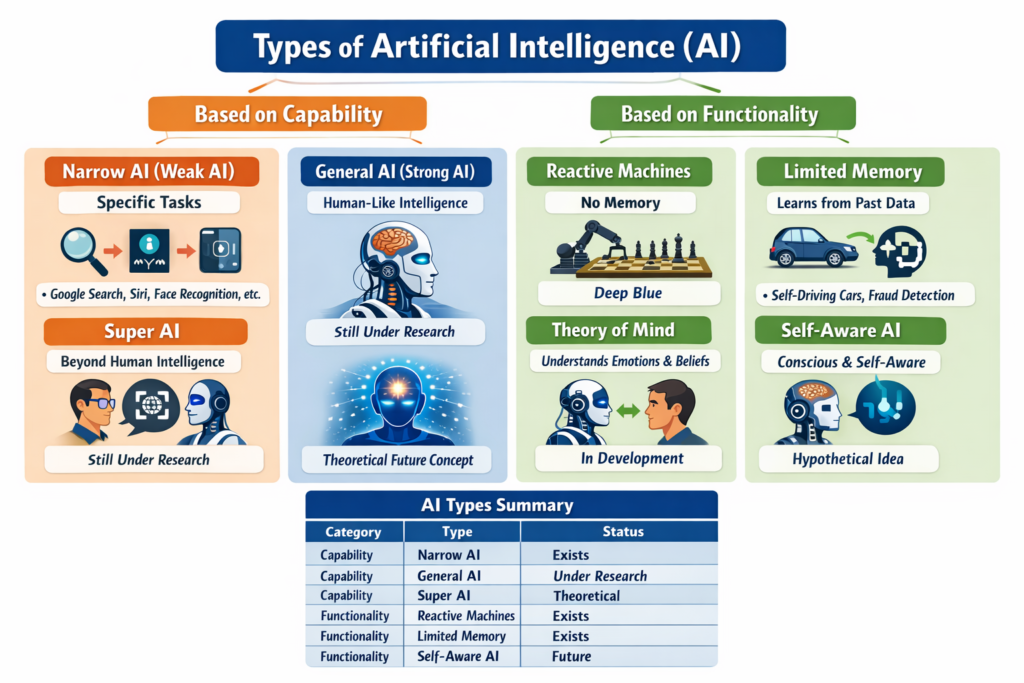
Classifying AI helps us understand its capabilities and limitations. Not every AI system can think, feel, or reason like a human. Some systems can only react, while others can learn and adapt. When we talk about the types of artificial intelligence, we’re essentially describing levels of intelligence and functionality.
This classification is useful for:
- Developers designing AI systems
- Businesses choosing AI tools
- Policymakers creating regulations
- Students and beginners learning AI fundamentals
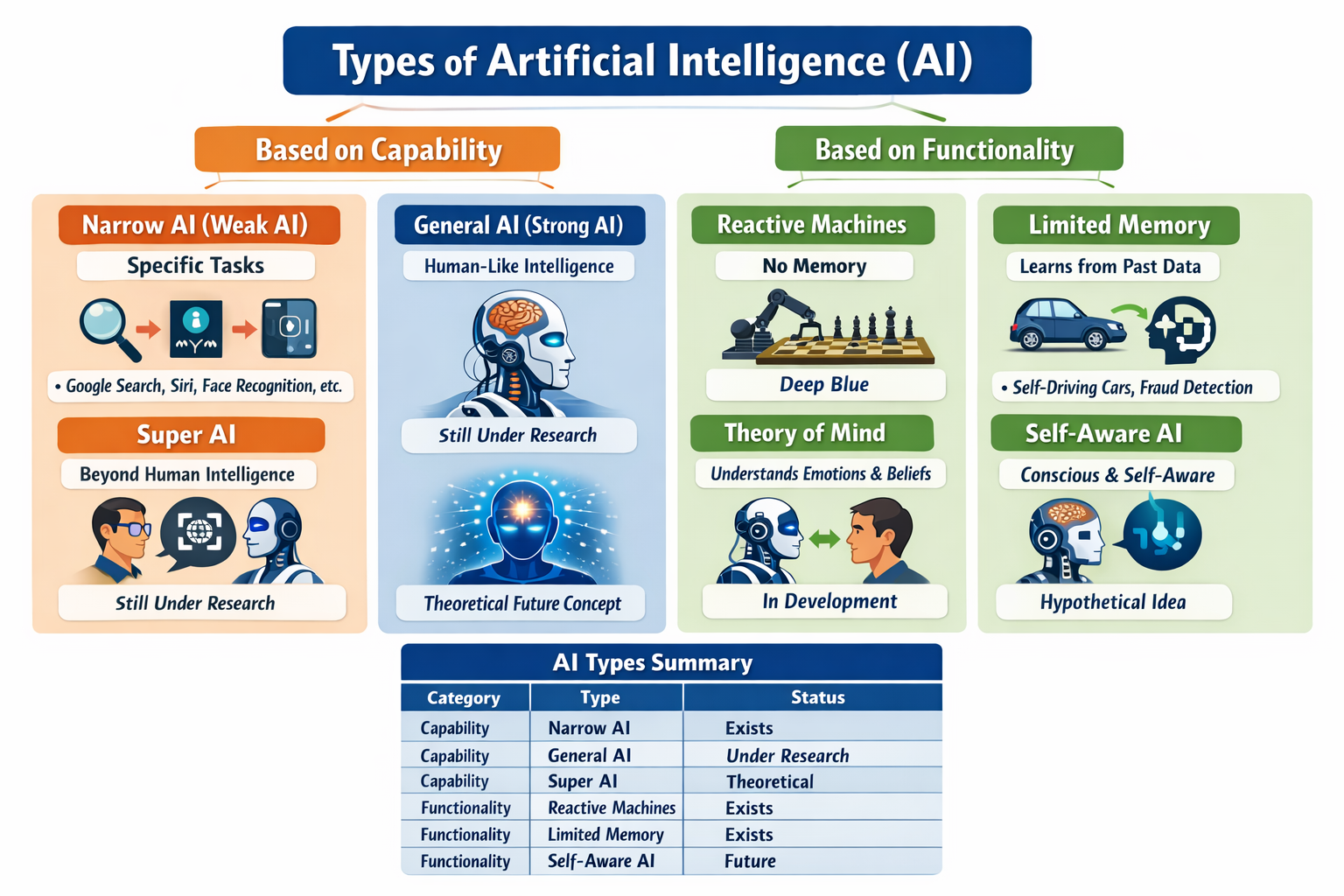
Type 1: Reactive Machines
Reactive machines are the most basic type of artificial intelligence. They do not store memories or learn from past experiences. Instead, they respond to current inputs based on predefined rules.
Key Characteristics
Reactive machines:
- Have no memory
- Do not learn from experience
- Always produce the same output for the same input
- Focus only on present situations
These systems are reliable and fast, but they’re also limited. They can’t improve over time or adapt to new situations.
Real-World Examples
A classic example is IBM’s Deep Blue, the chess-playing computer that defeated world champion Garry Kasparov. Deep Blue analyzed millions of possible moves but didn’t “learn” from previous games.
Other examples include:
- Simple recommendation engines
- Rule-based game bots
- Basic automation software
While reactive machines may seem outdated, they’re still useful where consistency and speed matter.
Type 2: Limited Memory AI
Limited memory AI systems can learn from past data for a short period. Most modern AI applications fall into this category. When people discuss practical types of artificial intelligence, limited memory AI is usually what they mean.
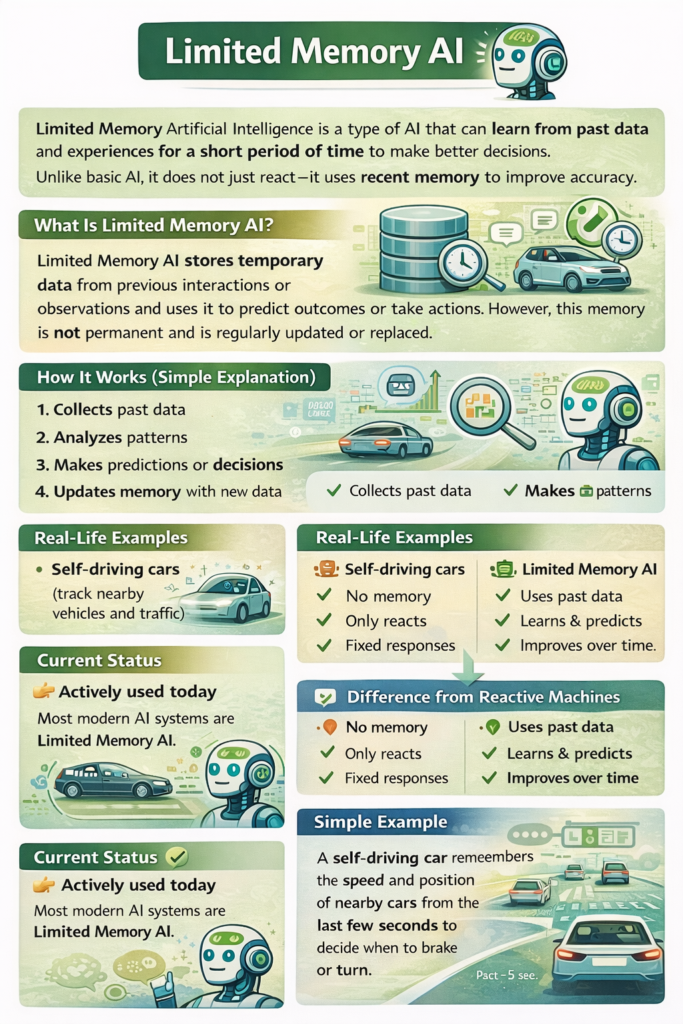
How Limited Memory Works
These systems:
- Use historical data for decision-making
- Improve performance through training
- Update models as new data comes in
However, the memory is temporary. Once the system is retrained or reset, old data may no longer influence decisions.
Applications in Daily Life
Limited memory AI is everywhere:
- Self-driving cars analyzing traffic patterns
- Voice assistants recognizing speech
- Fraud detection systems spotting unusual activity
- Recommendation systems on streaming platforms
Because of its flexibility and effectiveness, limited memory AI has become the backbone of today’s AI-powered world.
Type 3: Theory of Mind AI
Theory of Mind AI represents a more advanced and still-developing category. This type aims to understand human emotions, beliefs, and intentions.
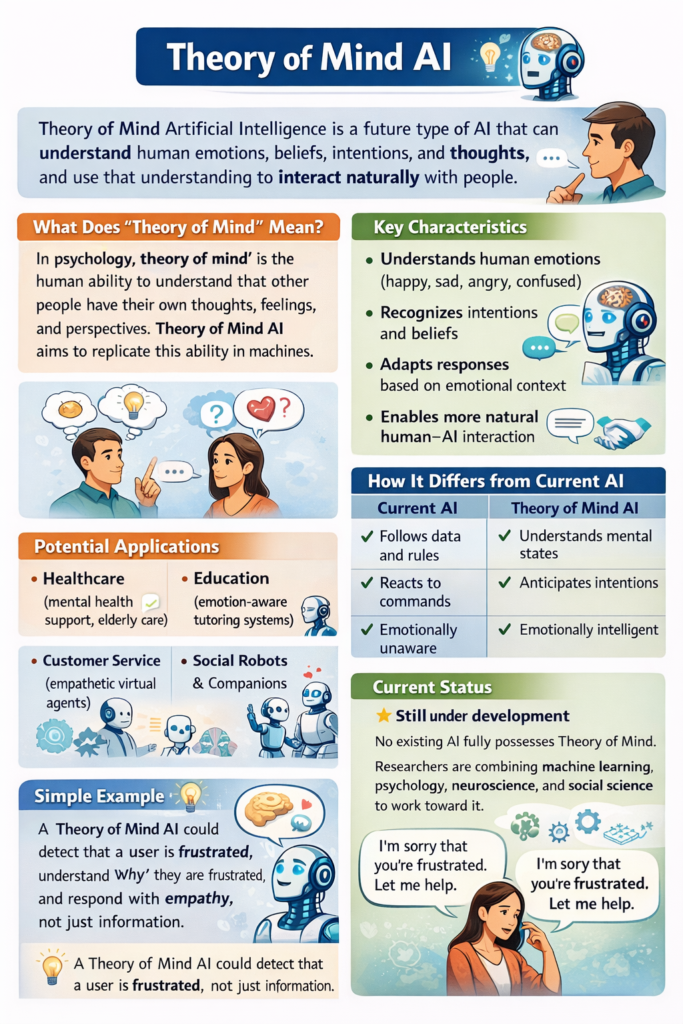
Concept and Research Status
Unlike reactive or limited memory systems, Theory of Mind AI would:
- Recognize emotional states
- Understand social cues
- Adjust behavior based on human feelings
As of now, this type of artificial intelligence exists mainly in research labs. Scientists are working on combining psychology, neuroscience, and machine learning to make this possible.
Ethical and Social Impact
If achieved, Theory of Mind AI could:
- Improve human–machine interaction
- Support mental health care
- Enhance education and training
However, it also raises ethical concerns, such as emotional manipulation and privacy risks. Responsible development will be critical.
Type 4: Self-Aware AI
Self-aware AI is the most advanced and hypothetical form of artificial intelligence. It refers to machines that possess consciousness and self-understanding.
Hypothetical Capabilities
A self-aware AI would:
- Understand its own existence
- Have emotions and desires
- Make independent decisions
This type of AI goes far beyond current technology and remains firmly in the realm of theory.
Challenges and Risks
The risks include:
- Loss of human control
- Ethical dilemmas
- Potential misuse
For now, self-aware AI is a topic for philosophers, futurists, and science fiction writers rather than engineers.
Functional Types of Artificial Intelligence
Beyond capability-based categories, the types of artificial intelligence can also be grouped by functionality.
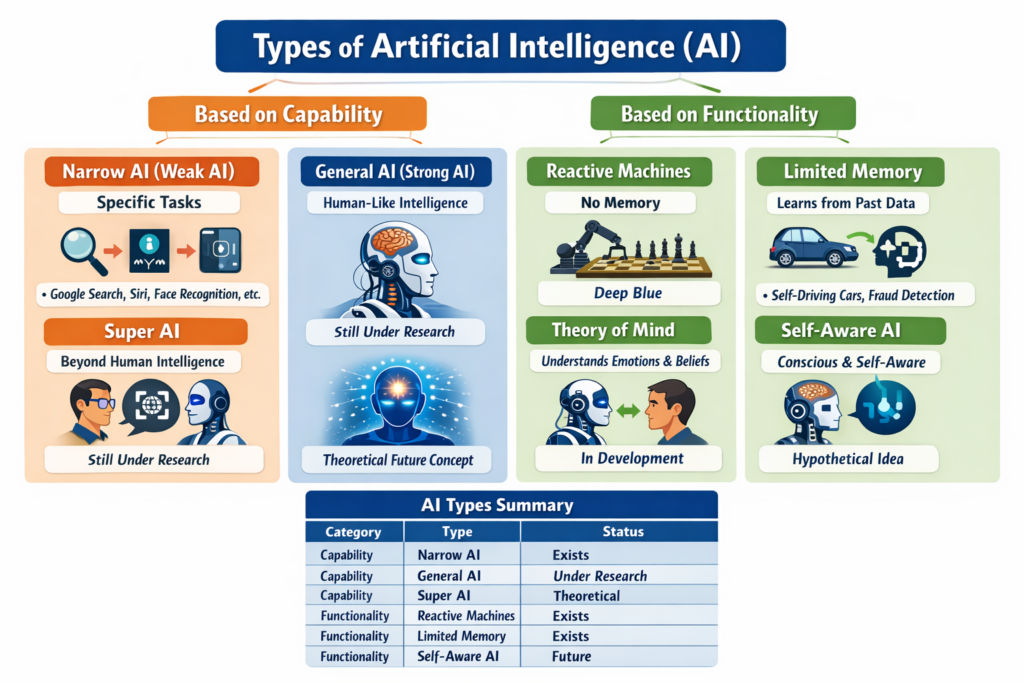
Narrow AI
Narrow AI, also called Weak AI, is designed for a specific task. Examples include:
- Chatbots
- Image recognition systems
- Virtual assistants
This is the only form of AI currently in widespread use.
General AI
General AI would perform any intellectual task a human can do. It would learn, reason, and adapt across different domains. Despite major progress, General AI has not yet been achieved.
Super AI
Super AI would surpass human intelligence in every aspect. While exciting, it also presents serious ethical and safety concerns.
Benefits of Different Types of Artificial Intelligence
Understanding different types of artificial intelligence helps us unlock their benefits:
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- Better decision-making
- Enhanced safety and accuracy
- Innovation across industries
When used responsibly, AI can support economic growth and improve quality of life.