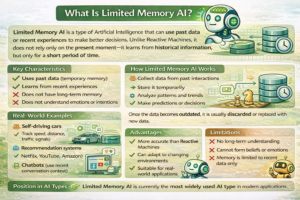
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers in such a way that the data cannot be altered without altering all subsequent blocks. In simple terms, it’s a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof way to store information.
At its core, blockchain removes the need for intermediaries like banks or centralized authorities. Instead, trust is established through cryptography, mathematics, and distributed consensus. Sounds complex? Don’t worry—we’ll break it down step by step.
Today, blockchain technology is not just about Bitcoin or cryptocurrencies. It’s reshaping industries like finance, healthcare, education, supply chain, and even government systems. And honestly, this is just the beginning.
History and Evolution of Blockchain
The concept of blockchain was introduced in 2008 by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto. The primary goal was to create a peer-to-peer electronic cash system—what we now call Bitcoin.
Key Milestones:
- 2008 – Blockchain whitepaper released
- 2009 – Bitcoin launched
- 2015 – Ethereum introduced smart contracts
- 2020–Present – Rise of DeFi, NFTs, Web3
Over time, blockchain evolved from a simple transaction ledger into a powerful programmable infrastructure. Today, enterprises and governments are actively experimenting with blockchain-based solutions.
How Blockchain Technology Works
Understanding what is blockchain technology becomes easier when you know how it works behind the scenes.
Blocks, Hash, and Chain Explained
Each block contains:
- Transaction data
- A timestamp
- A cryptographic hash
- The hash of the previous block
These blocks are linked together, forming a chain. If someone tries to change the data in one block, the hash changes, breaking the entire chain. That’s why blockchain is considered immutable.
Distributed Ledger System
Unlike traditional databases stored on a central server, blockchain uses a distributed ledger. Every participant (node) has a copy of the entire ledger. This ensures transparency and eliminates single points of failure.
Consensus Mechanisms
To validate transactions, blockchain uses consensus algorithms such as:
- Proof of Work (PoW)
- Proof of Stake (PoS)
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
These mechanisms ensure that everyone agrees on the same version of the truth.
Types of Blockchain Technology
Not all blockchains are the same. Depending on use cases, there are different types.
Public Blockchain
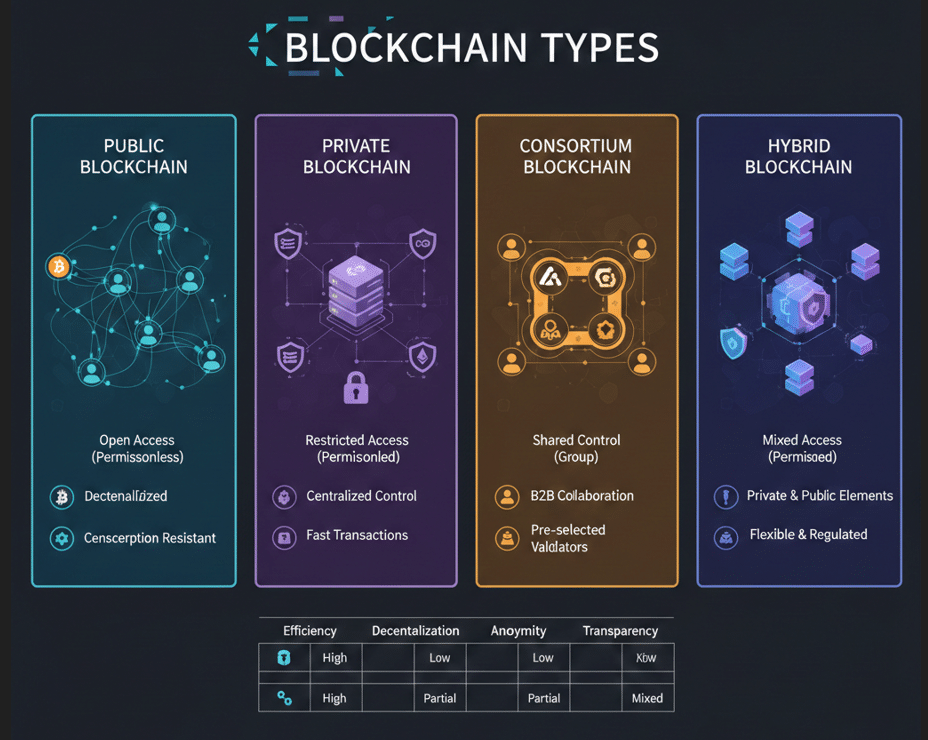
- Open to everyone
- Fully decentralized
- Example: Bitcoin, Ethereum
Private Blockchain
- Controlled by a single organization
- Faster and more efficient
- Used by enterprises
Consortium Blockchain
- Controlled by a group of organizations
- Semi-decentralized
- Common in banking systems
Hybrid Blockchain
- Mix of public and private
- Offers flexibility and control
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Some defining features include:
- Decentralization – No central authority
- Transparency – Publicly verifiable transactions
- Immutability – Data cannot be changed
- Security – Cryptographic protection
- Traceability – Easy audit trail
These features make blockchain technology highly reliable and trustworthy.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain offers several benefits:
- Reduced costs by eliminating intermediaries
- Faster transactions
- Increased trust and security
- Better data integrity
- Global accessibility
In short, it’s a game-changer for digital trust.
Disadvantages and Limitations
That said, blockchain isn’t perfect:
- Scalability issues
- High energy consumption (especially PoW)
- Regulatory uncertainty
- Limited adoption
However, ongoing innovations are addressing these challenges.
Blockchain vs Traditional Databases
| Feature | Blockchain | Traditional Database |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Decentralized | Centralized |
| Transparency | High | Limited |
| Security | Very High | Moderate |
| Immutability | Yes | No |
Real-World Use Cases of Blockchain
Blockchain in Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are the most well-known applications.
Blockchain in Banking & Finance
Used for cross-border payments, fraud prevention, and DeFi platforms.
Blockchain in Supply Chain
Ensures product authenticity and traceability.
Blockchain in Healthcare
Secures patient records and improves data sharing.
Blockchain in Education
Used for digital certificates and credential verification.
For more insights, you can explore IBM’s blockchain solutions:
👉 https://www.ibm.com/blockchain
| Industry | Pehle (Traditional) | Ab (Blockchain ke saath) |
| Banking | 2-3 din lagte hain transfer mein | Kuch seconds mein transfer |
| Luxury Goods | Nakli (Fake) products ka darr | QR code scan karke asliyat ka pata |
| Copyright | Artist ka kaam chori ho jata tha | Creator ko har baar “Royalty” milti hai |
Smart Contracts Explained
Smart contracts are self-executing programs that run on blockchain. They automatically enforce agreements when predefined conditions are met—no middlemen required.
Blockchain Security and Transparency
Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques like SHA-256 to secure data. Every transaction is visible and verifiable, making fraud extremely difficult.
Blockchain and Web3
Web3 represents the decentralized future of the internet, powered by blockchain. It focuses on user ownership, privacy, and censorship resistance.
Future Scope of Blockchain Technology
The future looks bright:
- Integration with AI and IoT
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
- Mass adoption in enterprises
Experts believe blockchain will become as common as the internet itself.
Career Opportunities in Blockchain
Popular roles include:
- Blockchain Developer
- Smart Contract Engineer
- Blockchain Analyst
- Web3 Consultant
With the right skills, blockchain can be a lucrative career path.